
This post originally appeared at Mother Jones.
As part of his proposal for dealing with the crisis of child migrants crossing the border, President Obama has asked Congress for $3.7 billion in funding that would be used for, among other things, hiring more judges for the nation’s 59 immigration courts. Those courts have been overwhelmed by the influx of kids coming to the United States without parents or other relatives. But they were overwhelmed even before the children started showing up, in large part because of Republicans’ unwillingness to fund and staff them like other federal courts.
For years, since the second Bush administration radically stepped up, and Obama continued, deportation efforts targeted at undocumented immigrants, advocates have been begging Congress to beef up the funding for the courts that must process those new cases. As far back as 2006, then-Attorney General Alberto Gonzales recognized that the immigration courts were woefully understaffed to process a backlog of cases that back then stood at 169,000. Gonzales called for more funding to increase resources for the courts, including adding more 40 judges.
But then his office proceeded to attempt to fill those jobs (and others at the Department of Justice) with political hacks who couldn’t make it through the Senate confirmation process to land on a regular federal court. (Immigration courts fall under the jurisdiction of the DOJ, and their judges don’t require Senate confirmation.) One example: Carey Holliday, a Louisiana delegate to the 2004 GOP convention who made headlines for trash-talking former Mother Jones editor Michael Moore, who was at the convention filing dispatches for USA Today.
Other Bush appointees had a distinctly pro-government bias. One judge, Thomas Roepke, appointed to a court in El Paso, Texas, in 2005, denied fully 96.3 percent of all asylum cases that came before him between 2007 and 2012, according to records obtained by the Transactional Records Access Clearinghouse (TRAC) at Syracuse University.
Before he got very far with the immigration judge hiring spree, Gonzales resigned under fire for politicizing hiring at the DOJ, and by 2008, the immigration courts had eight fewer judges than when Gonzales launched his clarion call.
Meanwhile, while guys like Holliday were taking slots on the immigration bench, poor working conditions, crushing caseloads, and the overly politicized nature of the appointment process left the courts hemorrhaging other judges during the Bush administration. By the time Obama took office, immigration courts had a vacancy rate that reached 1 in 6 judgeships. The new Obama administration began hiring judges furiously, eventually adding an additional 44 new bodies to the immigration bench. Even so, his concurrent move to step up border enforcement meant that the deportation caseloads were growing even faster:
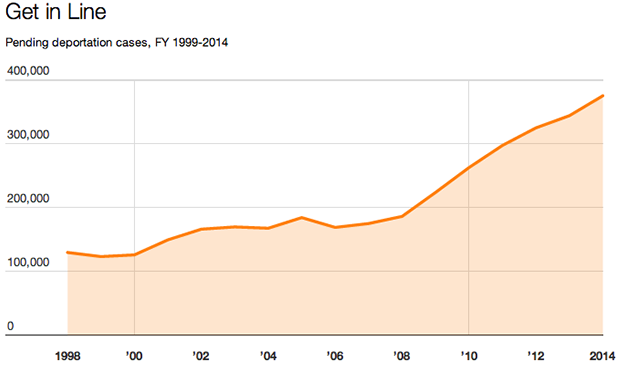
Created with Datawrapper. Source: TRAC. Get the data.
Immigration judges can expect to handle 1,500 cases at any given time. By comparison, Article I federal district judges handle about 440 cases, and they get several law clerks to help manage the load. Immigration judges have to share a single clerk with two or three other judges. The lack of staffing creates an irony that seems to be lost on the current Congress: Too few judges means that people with strong cases languish for years waiting for them to get resolved, while people with weak cases who should probably be sent home quickly get to stay in the United States a few years waiting for a decision.
That dynamic is only getting compounded with the recent influx of unaccompanied juveniles, who usually don’t have lawyers to represent them in court. “It’s ironic and counterintuitive that we should not give enough money to the system to allow it to work more quickly,” says Dana Marks, an immigration judge in San Francisco and president of the National Association of Immigration Judges.
In 2010, the American Bar Association called on Congress and the White House to immediately initiate the hiring of at least 100 new judges to help relieve the existing crisis in the courts. Instead, Congress failed to deal with the budget of any agency, sequestration happened, and the Justice Department started a hiring freeze that didn’t end until December 2013, even though at least 100 sitting immigration judges are eligible to retire this year. Meanwhile, the comprehensive immigration bill passed in the Senate last year would have added 225 new judges to the immigration courts over three years (along with clerks and support staff), but Republicans killed the bill in the House.
Today, there are 243 judges — just 13 more than in 2006 and 21 fewer than at the end of 2012 — and more than 30 vacancies the government is trying to fill. All this despite the fact that the immigration court backlog has increased nearly 120 percent since 2006. And that was before the kids started coming. Last week, TRAC reported that the official immigration court backlog in June hit 375,503, up by 50,000 since the start of 2013. Among the languishing cases: more than 12,000 kids each from Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. All told, more than 40,000 cases in the current court backlog involve children, and the numbers are growing. The average time an immigration case has been pending is now up to 587 days:

Created with Datawrapper. Source: TRAC. Get the data.
Marks says the long-running court crisis has hindered judges’ ability to respond to what’s happening with the onslaught of unaccompanied kids. “The whole problem with this surge,” she says, “is that it has occurred on top of a crisis in the court that no one was talking about.”
Obama is trying to change that equation. His budget request would add 40 new judges to the 35 he has already requested for next year, with the goal of creating enough capacity to handle an additional 55,000 to 75,000 cases a year. But the disconnect between what the country spends apprehending and detaining undocumented immigrants and what it spends processing them is still stark. While Obama has requested an additional $64 million to fund the immigration courts, that figure is dwarfed by the $1.5 billion he requested for border security and Immigration and Customs Enforcement.
In the end, the extra enforcement funding is likely to generate so many new cases that any judges added to the court will be just as backlogged as the ones there now, offering little hope of speeding up the process for all those kids currently languishing in border detention centers.


