This post first appeared at Mother Jones.
Last week, an energy analyst at Deutsche Bank came to a startling conclusion: By 2016, solar power will be as cheap or cheaper than electricity from the conventional grid in every state except three. That’s without any changes to existing policy. In other words, we’re only a few years away from the point where, in most of the United States, there will be no economic reason not to go solar. If you care about slowing climate change or just moving toward cleaner energy, that is a huge deal.
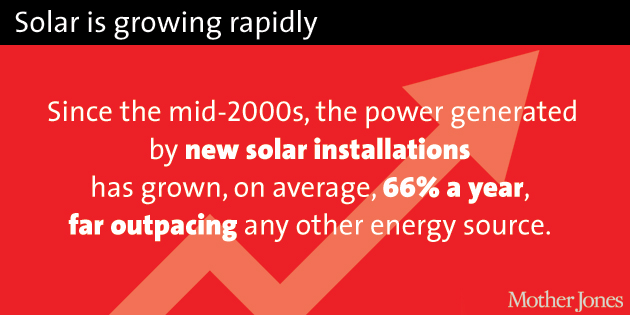
And solar energy is already going gangbusters. In the past decade, the amount of solar power produced in the United States has leaped 139,000 percent. A number of factors are behind the boom: Cheaper panels and a raft of local and state incentives, plus a federal tax credit that shaves 30 percent off the cost of upgrading.
Still, solar is a bit player, providing less than half of 1 percent of the energy produced in the United States. But its potential is massive — it could power the entire country 100 times over.
So what’s the holdup? A few obstacles: pushback from old-energy diehards, competition with other efficient energy sources, and the challenges of power storage and transmission. But with solar in the Southwest already at “grid parity” — meaning it costs the same or less as electricity from conventional sources — Wall Street is starting to see solar as a sound bet. As a recent Citigroup investment report put it, “Our viewpoint is that solar is here to stay.”
Some numbers that tell the story:

Sources
Solar growth: Solar Energy Industries Association
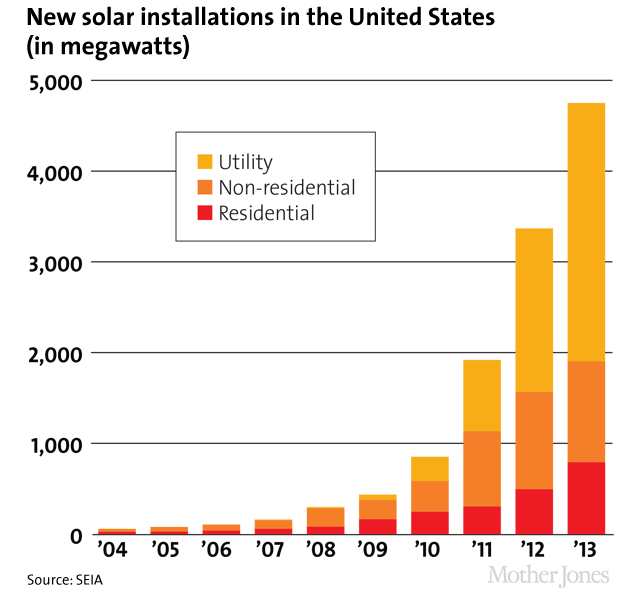
New solar installations: SEIA
Sunlight: Sandia National Lab, Energy Information Administration/National Renewable Energy Laboratory
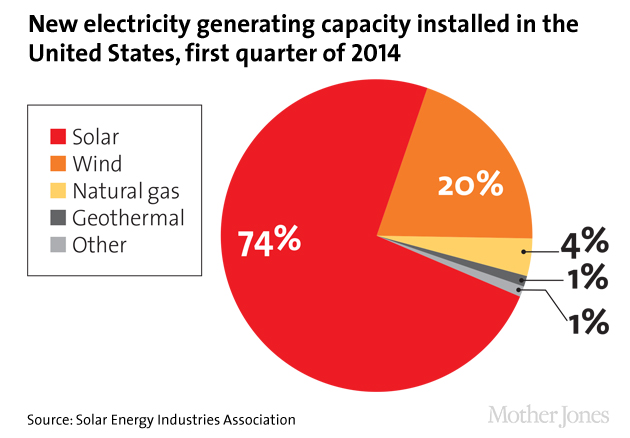
Electricity generating capacity: SEIA
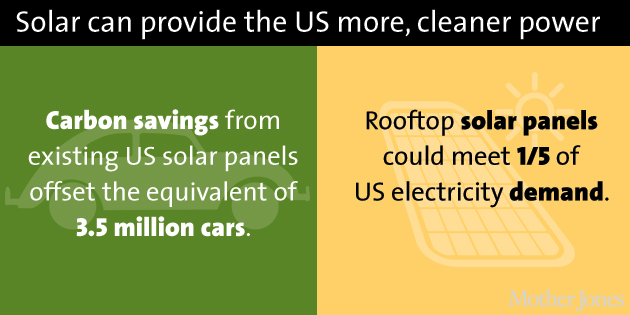
Carbon savings, electricity demand: SEIA, EIA/NREL
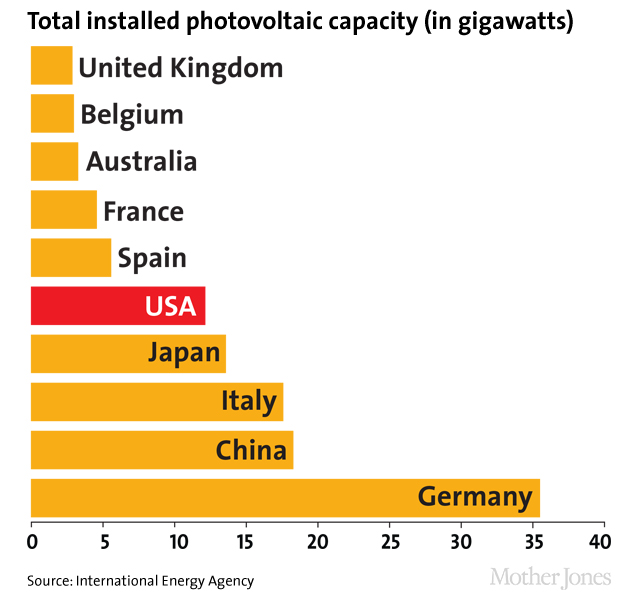
Installed PV capacity: International Energy Agency
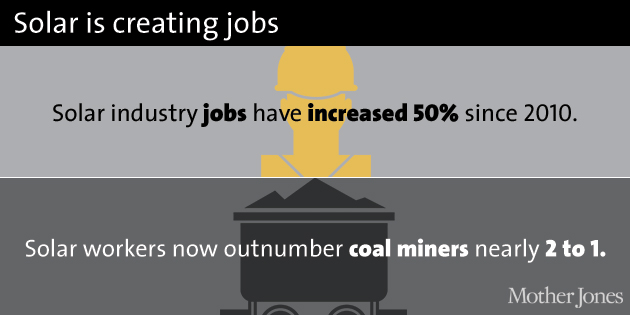
Solar jobs: The Solar Foundation, Bureau of Labor Statistics
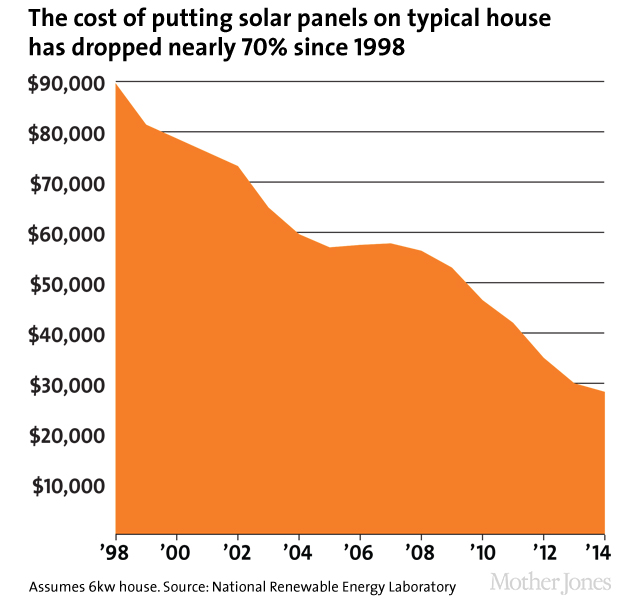
Solar panels on a typical house: NREL
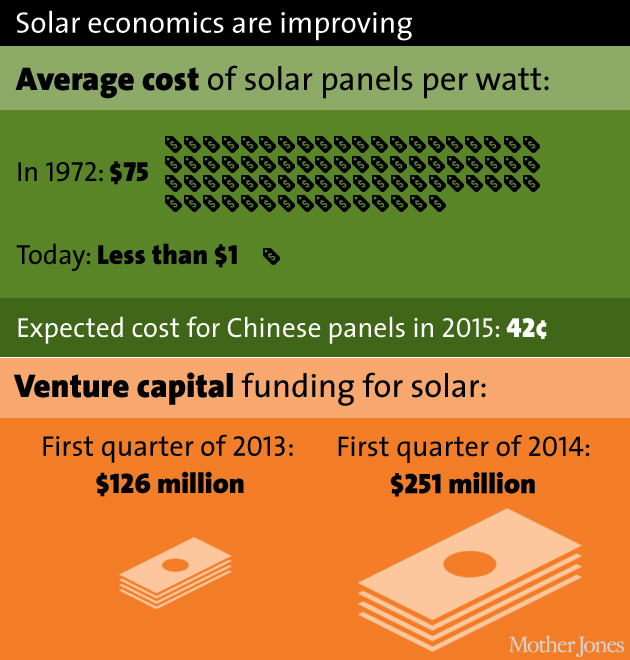
Panel cost, VC funding: Greenpeace; Mercom Capital Group (2013 & 2014)
(Image credits: Shutterstock (Earth, USA); Maurizio Fusillo/Noun Project (solar panel); Okan Benn/Noun Project (car); Q. Li/Noun Project (chart); Sergey Krivoy/Noun Project (coal trolley); Marcio Duarte/Noun Project (worker); Alex Berkowitz/Noun Project (cash))



