Tyler Tabor with his son, D.T. (Photo courtesy of the Tabor family.)
This post originally appeared at Mother Jones.
When Tyler Tabor was booked in a jail outside Denver on a spring afternoon in 2015, he told a screening nurse that he was a daily heroin user and had a prescription for Xanax. A friendly, outdoorsy 25-year-old with a son in kindergarten, Tabor had started using opioids after he injured his back on the job as a welder. When he was arrested on two misdemeanor warrants, his parents decided not to pay his $300 bail, thinking he would be safer in jail and away from heroin for a few days.
Three days later, Tabor died of dehydration at the Adams County jail, according to a coroner’s report. The alleged cause: drug withdrawal.
A lawsuit filed by the Tabors against the county and Corizon Health, the jail’s private health care provider, describes in chilling detail the three days of missed opportunities and seemingly callous medical care. It draws on video footage, some of which is shown below, from a surveillance camera in Tabor’s cell. By the end of the first day in jail, Tabor was in the throes of severe withdrawal: vomiting, diarrhea, low blood pressure. He was too dehydrated to provide a urine sample. A day later, he could no longer walk or unclench his fingers. When a nurse came by to give him the usual withdrawal medications — a cocktail of things like Gatorade and Pepto Bismol — he fell to the ground, trembling. Later that night, he begged for an IV — he knew from a previous detox that withdrawing from the combination of heroin, an opioid, and Xanax, a benzodiazepine, was particularly risky. But, according to the complaint, he was told IVs were only used when “absolutely necessary.” He died six hours later, leaving behind a wife and a 5-year-old son.
“A simple IV would have almost certainly saved his life,” reads the complaint.
Adams County officials declined to comment on the case. Martha Harbin, a spokesperson for Corizon Health, said the allegations in the complaint were “inconsistent with the known facts.” She added, “It certainly is not our policy to deny a patient appropriate and indicated treatment.”
Yet as the nationwide opioid epidemic continues to spiral, more and more inmates who use heroin, painkillers or methadone are showing up in jails across the country, where withdrawal treatment can be rudimentary. “So many more people are coming in hooked on opioids,” says David Lane, the attorney representing the Tabors. “If the jails are not trained and they’re not ready for it, you get a Tyler Tabor.”
No organization tracks how many people have died from drug withdrawal in jail, but Mother Jones found 20 lawsuits filed between 2014 and 2016 alleging that an inmate died from opiate withdrawal complications. That number likely represents just a fraction of all jail withdrawal deaths, Lane says. In addition to the counties, many families also sue the companies that public jails often contract with to provide health care—like Corizon Health, in the Tabors’ case.
By the time of Tabor’s death, in May, at least four other inmates in jails around the country had died that year from complications of opiate withdrawal, according to lawsuits filed by their families. In March, 37-year-old Jennifer Lobato was booked into Colorado’s Jefferson County jail, just a half hour from where Tabor would die, for shoplifting $57 of merchandise from Old Navy with her son. A guard scoffed at Lobato, a regular heroin user, as she vomited before collapsing, according to a subsequent investigation by the sheriff’s office. A month later, an 18-year-old aspiring artist named Tori Herr collapsed in Pennsylvania’s Lebanon County jail. “I just want something to drink,” she said to her mom on the phone days before she died. “I want lemonade.”
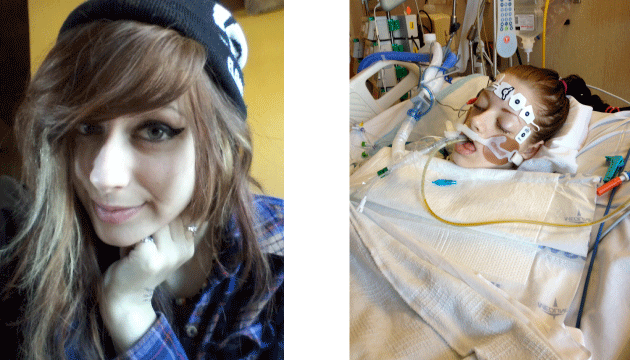
Left: Tori Herr as a high schooler. Right: Herr in the hospital after withdrawal in jail. (Photos courtesy of the Herr family.)
Jefferson County settled the Lobato case for $2.5 million last fall. County spokesman Mark Techmeyer said the jail’s withdrawal treatment and evaluation protocols changed in response to Lobato’s death; Lebanon County officials declined to comment on the Herr case.
Outside of jails, dying from opiate withdrawal is exceedingly rare because, with few exceptions, it is so preventable. Dehydration, the withdrawal symptom that usually kills people, can be treated with intravenous fluids. It’s nearly unheard of to withdraw from opioids without slowly tapering or having emergency medical care, says Kevin Fiscella, an addiction specialist who sits on the board of the National Commission on Correctional Health Care (NCCHC), which accredits correctional health services. “What’s happening in jails, it’s kind of a natural experiment to see what happens,” he says. “And in fact some people do die.”
When a user quits opioids cold turkey, the body quickly starts to experience the opposite effects of the original drug, resulting in a rarely fatal but often tortuous withdrawal process that can persist for days or weeks. Where opioids reduce pain, withdrawal makes the body hypersensitive to it. Opioids induce euphoria; withdrawal feels like the world is going to end. Opioids cause constipation; withdrawal causes diarrhea and vomiting. If a person going through withdrawal can’t keep fluids down and is not given an IV, he or she can succumb to dehydration.
Fiscella notes that a number of factors can make withdrawal behind bars risky. Inmates don’t always tell nurses during the screening process that they’re drug users; sometimes, withdrawal kicks off a domino effect that makes other health conditions, like heart problems, act up. Lots of opioid users are also on benzodiazepines like Xanax or Valium, known for enhancing and extending the effects of heroin, painkillers or methadone. Benzodiazepines can make withdrawal much more dangerous.
What’s more, many cash-strapped jails lack basic medications or medical equipment like IVs. And often, Fiscella says, there simply aren’t enough health care staff to check in regularly on each and every withdrawal patient. “In a lot of these deaths, people were simply ignored,” he says.
Of the 20 alleged opiate withdrawal deaths in jails that Mother Jones found, five occurred in jails served by a privately held company called Correct Care Solutions. Based in Tennessee, CCS is one of the country’s largest correctional health care services, providing medical services to 250,000 patients in jails, prisons, state hospitals and forensic treatment centers throughout the country.
In 2015, the company brought in nearly $1 billion in revenue, according to the Nashville Business Journal. CCS President Patrick Cummiskey told the Journal that the company had “grown 20 percent-plus annually since inception, so growth is our norm.”
Seven Charts That Speak Volumes About the Opioid Epidemic (Mother Jones)
Despite the company’s robust finances, treating withdrawal can fall through the cracks, according to four jail nurses who currently or recently worked for Correct Care Solutions. Their names have been changed to protect their privacy.
During the evening shift at the Brown County jail in Green Bay, Wisconsin, there is one nurse—and no other medical staff—for roughly 700 inmates, according to nurses who worked at the facility. “I had people detoxing, I had people with chest pain, I had people getting into fights, I had emergencies where people aren’t breathing,” said Abby, who worked at the facility for nine months before leaving last fall. “I can’t assess somebody three times a shift when there’s one nurse for 700 inmates, and do a meaningful assessment, and also provide interventions when I have 20 people on opiate withdrawal.”
Abby says she bought her own medical supplies because the blood pressure cuffs, thermometers, and stethoscopes provided by CCS didn’t always work. She often found herself stuck between a rock and a hard place: There was no IV therapy in the jail, but sending inmates to the hospital was frowned upon. In order to send a withdrawal patient to the hospital, she said, the inmate would “need to be at the point where their vital signs were dropping, their internal organs were starting to become compromised.”
Abby left CCS last fall because she was worried that the quality of care at the jail was so low that she was violating her nursing license. “If I was called into court, I couldn’t say truthfully that I am providing good nursing care,” she said.
Brown County declined to comment for this article.
Greta, a nurse at a different jail served by CCS, described a similar scene. During a typical medical check, Greta had about 30 seconds to take an inmate’s vital signs, hand out medications and gauge withdrawal symptoms — often in dim lighting and always standing next to a deputy jail guard. On top of it, she said, “You’re using your eyes and your ears because you don’t really have technology. You’re lucky to have a blood pressure cuff.”
Asked about the allegations, CCS spokesman Jim Cheney wrote in an email to Mother Jones, “While it is very difficult to respond to an anonymous source when determining the credibility of their assertion, CCS employs regional executives across the country to ensure that the service standards we have established are upheld. It is difficult to imagine a scenario in which a facility was not provided the instruments necessary for routine health care, and should there be a need, our nurses have immediate and direct access to administrative teams who can facilitate those resources in short-order.” He added that the staffing ratio is determined by “facility capabilities,” and the company does not frown upon the use of outside providers. In the event that the medical needs of an inmate fall beyond what the facility can provide, he said, “we rely on our medical partners in the community for support.”
But in some cases no one calls for support before it’s too late. A video strikingly similar to that of Tabor shows David Stojcevski, a 32-year-old from outside Detroit, losing 50 pounds over 16 days of vomiting, diarrhea and trembling on the ground before his death in the summer of 2014. Stojcevski had been booked at the Macomb County Jail, also served by CCS, for being unable to pay a $772 fine for driving carelessly. Though he notified nurses of his prescriptions to methadone and Xanax, an opioid and a benzodiazepine, respectively, he never received either medication in jail, according to a lawsuit later filed by his parents.
A Department of Justice investigation of the case found no criminal wrongdoing on the part of Macomb County or CCS, saying there wasn’t enough evidence that jail staff acted with criminal intent to prosecute the case. The lawsuit filed by the family is ongoing; county officials declined to comment on the case. Cheney described CCS’s withdrawal protocol as “one of most advanced and respected in the industry,” adding that CCS follows standards from the NCCHC and the American Correctional Association. He added that “while tragic situations do occur, there are exponentially more circumstances in which our professionals save lives and improve the health of the individuals that they treat.”
Corizon Health, the health care provider in Tabor’s case and the nation’s largest privately held correctional health company, is currently facing at least one other lawsuit alleging an opiate withdrawal death. A year before Tabor died, Madaline Pitkin, a 26-year-old from Portland, Oregon, died of heroin withdrawal after repeatedly requesting help on medical forms, according to a lawsuit filed by her family. In her final request, she wrote, “This is a third or fourth call for help. I haven’t been able to keep food, liquids, meds down in six days … I feel like I am very close to death. Can’t hear, seeing lights, hearing voices. Please help me.”
Harbin, the Corizon spokesperson, declined to comment on the specifics of Tabor’s or Pitkin’s cases because of active litigation and patient privacy rules. “One of the most common misconceptions about our company is that we somehow benefit from providing lower quality care,” she wrote in an email. “To the contrary, what makes good medical sense and good business sense is proactive preventive care—intervening early to treat conditions before they become serious and more costly to treat.”
Tabor’s family, meanwhile, is still reeling from their loss. Tyler’s son, D.T., an energetic 6-year-old who loves fishing and biking, still regularly asks when his dad will come home. Tyler’s father, Ray, a manager at the local Safeway, tells D.T. that he went to heaven. “It’s one thing to lose a child,” says Ray. “But it’s another thing knowing that he died in a jail cell alone on the floor, asking for help.”