
Katharine Hayhoe (Courtesy of katharinehayhoe.com)
On Monday, Aug. 7, before North Korea, and before Charlottesville, you might recall that The New York Times published an article entitled “Scientists Fear Trump Will Dismiss Blunt Climate Report” that kicked up a storm of press coverage. The draft report on the state of science relating to climate change and its physical impacts is part of the National Climate Assessment (NCA), which is congressionally mandated every four years.
Two days later, Washington Post reporter Eric Wemple wrote that The Times was “guilty of a large screw-up” on the story, because Times reporter Lisa Friedman gave the impression that the report had been leaked. Trouble was, the copy of the report that The Times originally presented alongside the story was a draft that had been publicly available since December. (The Times eventually updated the PDF with a different version of the report, one that had previously not been available to the public.)
We spoke with one of the report authors, climate scientist Katharine Hayhoe, who is a professor in the department of political science and director of the Climate Science Center at Texas Tech University. This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
TR: Can you explain what happened with the Times report and the different drafts?
KH: Yes, it’s so confusing, isn’t it? But yes, I can tell you exactly what’s going on. So, on Monday, [Aug. 7] I was contacted by Lisa Friedman, who wrote The New York Times article, saying that she would like to talk to me. I sent her some brief comments about how it was possibly the most comprehensive and conclusive and definitely the most up-to-date climate science report ever published in the United States — in the entire world, really, because the IPCC report is now 4 years old.
Then the article came out, and it was clear that the quote she used and the PDF they posted to accompany it were from the third-order draft, which was released for public comment in December of this past year. It’s still publicly available via the National Academy website. Although, I would venture to say, probably, that upward of a thousand more people have now read it than ever read it any time in the past six months!
— Katharine Hayhoe
So, I pointed that out [via Twitter] because it’s very important, No. 1, just from an accuracy perspective, but, No. 2, because this was definitely being framed as, “Oh, all of these scientists were so afraid it was getting to be suppressed that they leaked this document.” I don’t know what scientists those were, and it didn’t necessarily have to be scientists. This document, our draft, has been available to hundreds of people in government agencies as well in all these other offices.
And then The New York Times uploaded a PDF of the fifth-order draft — the final draft that is currently under final review. The differences between the fifth-order draft and the fourth-order draft are primarily — not entirely, but primarily — the author’s responses to the very extensive National Academy of Sciences review, which [by the way] was incredibly constructive. The main messages, the main conclusion didn’t change, but there were definitely substantial changes to the content of some of the sections.
This report is so thoroughly reviewed. It has public review, peer review, agency review — the National Academy convened a special committee only to review this report. Their review was about as long as the report itself! So, that’s the difference between No. 3 and No. 5, and The New York Times has released No. 5.
I do understand that this was confusing, and it was certainly written one way and implied certain things, but at the same time, the final review phase is a point at which, in the past, going back to the Bush era, that is the point at which the political edits have happened.
TR: Interesting, OK. But it does seem then that somebody did leak the fifth version, right?
KH: Yes, that is correct. The original article and the original PDF were for the third version, but then subsequently they did post the fifth version, which means that somebody did send that to them. Like I said, though, there are headlines all across the world saying, “Scientists leak report, fearing it will be suppressed.” This report is accessible to hundreds of people, it only takes one person to push the button. Most of our offices, at least the people that I talked to, were actually feeling pretty good at the way the review was going so far. We did not have any indication that there were going to be any political [changes].
TR: Can you talk about how the two reports are different from the previous one (NCA3, released in 2014) to this one? What are the major points that you would say that you came up with?
KH: No. 1, this climate science report is much more comprehensive. It covers the entire gamut. It doesn’t just talk about temperature and precipitation fields, it [also] talks about new cutting-edge emerging science on how human-induced climate changes interacted with our weather patterns, with ocean circulation. It also talks about what’s going to be required if we’re going to meet the Paris Agreement. What’s the carbon budget remaining if we’re going to stabilize climate change? And then it talks about the potential for surprises in the climate future. What are the things that we know we don’t know, what are some of the things that we possibly don’t even know that we don’t know about this? What’s the chance of things turning out very differently than we expect, and what’s the chance of those surprises being negatives? And we concluded that the chances are pretty high, that surprises would be negative rather positive.
There’s a whole chapter not just on ocean acidification but also on ocean warming, which we don’t think about as much, but it can be even more important in [terms of] impact. And, then, also on the fact that oxygen levels are dropping in large parts of the ocean, which is very concerning as well.
TR: The report states that significant advances have been made in the attribution of human influence for individual climate and weather extreme events since the last report. It sounded like the most interesting advances were made in what is called attribution science. Can you explain a bit about that?
KH: Yes, that’s looking at individual events. [For example,] how did human-induced climate change contribute to the California drought? And the general conclusion is that the onset of the drought was part of natural variability, but the fact that this drought occurred over much warmer conditions, led to an enhancement of what they call the ridiculously resilient ridge. When a weather system that could possibly produce rain came along and hit that ridge, it would often get pushed up or pushed down but it couldn’t pass through and go over California. That ridge was enhanced and held in place for much longer than it would be otherwise by the abnormally warm temperatures. So there was this vicious cycle — the warmer it gets, the drier it gets, the drier it gets, the warmer it gets. That’s just one example of the way that we’re actually starting to, as they say, detect a human finger print in individual events.
TR: The report assessed 10 different US regions. What do you think were the regions that are suffering the most right now from climate change? Because that seemed to be another major finding, that we’re already seeing the affects.
— Katharine Hayhoe
KH: Yes, well, when you say suffering, the climate science report specifically looked at physical changes in climate systems. We have to wait until the regional and sectoral chapters have been have done to actually talk about impact… So, that said, the way that climate change affects us in the places where we live, 99 percent of the time, is exacerbating the risks we already face today. If you look at the risks that we face in the places where we live, more often than not, many of those risks are being exacerbated.
In the US Northeast, they have seen significant increases in heavy precipitation events that are increasing their flood risk. If you look at Florida, our report talks about the sunny day flooding and the increase in the heavy precipitation events. In Texas, we’re at risk of hurricanes, which are getting stronger as we’ve got the warmer ocean water. We also have regular patterns of drought and flood that are being exacerbated by warmer conditions that accelerate the rate of evaporation. We talk about what things we do see trends in and what things we don’t. We don’t see trends in drought frequency, but we do see trends in the frequency of heavy precipitation events. The bottom line is, wherever we live, we experience climate change in the way that it’s exacerbating the weather and climate risks that we already face today.
NOAA has this really awesome map that shows how many weather and climate events that have cost over a billion dollars in damage have occurred in each state since 1980. And when you look at that, it’s really interesting, because the No. 1 state that has had the most number of million-plus dollar weather and climate events is Texas. And, now, let’s be clear, climate change is not causing all of these events, but climate change is interacting with and exacerbating many, not all, but many of these events, making them stronger than they would be otherwise, increasing the damages of these events in many cases.
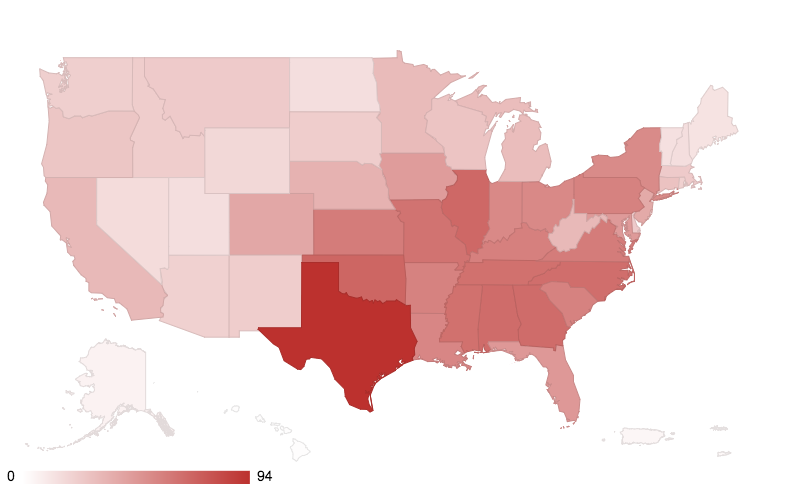
Please note that the map reflects a summation of billion-dollar events for each state affected (i.e., it does not mean that each state shown suffered at least $1 billion in losses for each event).
*as of July 7, 2017 (NOAA)
So, this map, it shows you two things. It shows you which states are already naturally vulnerable and then which states are also in the front lines when it comes to climate change exacerbating the weather extremes.
TR: Texas is bright red. And that’s due to storms mostly?
KH: Oh, it’s due to a whole lot of things. It’s because Texas gets everything. Texas gets ice storms and blizzards, they get derechos and windstorms, tornadoes, hail, hurricanes, droughts, flood, everything — the only thing we don’t get really is snowmelt-related floods. Everything else we get.
TR: Since the report indicates that our lives are already being affected by climate change, do you think that Americans know that climate change is a culprit, and if not, how do we get them to know?
KH: Well, you’re probably familiar with the Yale climate opinion maps, right?
TR: Yes.
— Katharine Hayhoe
KH: They really are fascinating because they ask people all kinds of questions and then you can view the response to the questions across the whole country, by congressional district, by state, by county. People focus very much on the question, “Do you think this is real?” “We believe in climate change.” The whole thing is like it’s some religion. But what absolutely fascinates me is that as you go through the maps, the ones that ask people about [climate change] solutions are dark orange all across the entire country, which means everybody says “yes” to the solutions that they’ve asked people if they agree with. The one that is the darkest blue across the entire country means most people said “no” to this question: “Do you think global warming is affecting your life personally or will affect you in the next 15 years?” Nobody thinks it is or it will.
TR: Yes, that’s incredible.
KH: And that’s why I think the National Climate Assessment is so important, because it takes climate science down to the individual states and cities that people live in and it says, “This is what’s happening in your back yard or your front yard. This is what we expect to happen, this is the way it’s going to impact your agriculture, your economy, your water resources, your energy, your health, national security.” It brings it down to the level we see — it’s not about the polar bears, it’s what you’ll be. Is this is the world that you want to live in?
TR: And when do those regional reports come out?
KH: They’re due up next year.
TR: In order to get the word out to people so they understand the personal impact, who do you think needs to up their game? Is it scientists or the media or political donors?
KH: Yes, that’s a great question. I’ve been part of three National Climate Assessments so far: No. 2, No. 3, and then this one that we’re working on right now. And in the past, the National Climate Assessment has pretty much gone according to schedule; there’s no leaks, there’s nothing that’s getting any coverage ahead of time.
We finished the report, we got the website done, we crossed our t’s, dotted our i’s, got all the nice figures ready, got our talking points ready and then we all sat down in a big room and we were all like, “OK, bring on the media.” And, you know, people who were already were concerned about climate change would be there — Climate Wire and EEM, E&E News… and papers with science writers like The Washington Post and The New York Times would all do their dutiful write-ups and do an article. But that was pretty much it.
I mean, I have never had a day like I had [last] Tuesday, where every single network on the planet, [laughs] it seemed, from Al Jazeera to CNN to Fox News even, was calling saying, “We want to talk about this, can you be on camera in a few minutes?” I mean, that never happened before.
Isn’t that interesting? Because from the beginning from NCA2 that I was involved in — actually even NCA1 — the US Global Change Research Program hired the best science writer in the business. They hired the best communications team they could find. They created the best graphics. They created the best government website I’ve ever seen — it’s an accessible, friendly, up-to-date format. They made videos, they did communication training for the authors. Over the years, they’ve done everything they can. I can’t think of a single thing that the US Global Change Research Program could have done more than what they’ve done over the years in terms of trying to improve their ability to communicate this.
But when we got together to communicate this thing, CNN never showed up. TIME never showed up.
— Katharine Hayhoe
TR: So The New York Times and their “sort of” leak story really lit a fire under notice of this report as compared to the past.
KH: Yes, yes, they struck a chord, with words like “leak” and wanting to know the cracks in [the Trump administration] and things like that. My colleagues and I have been joking that from now on, we realize what went wrong in our communication program. What went wrong is we didn’t put the report in a brown paper envelope marked TOP SECRET and slide it under somebody’s door in the middle of the night [laughs]. So we’ve been joking about how we’re going to have completely different communication plans from now on. All our peer-reviewed journal articles are going to be stamped, SECRET — NOT FOR CITATION OR DISTRIBUTION. And we’re going to accidentally drop them in a coffee shop. [laughter]
TR: [laughs] That’s great.
KH: Yes, if you want to keep something secret, all you have to do is have a public review/comment period because clearly nobody will ever read it.
TR: One thing that is interesting about the report is that it doesn’t make any policy recommendations, right? Pure science?
KH: Actually, that was very deliberate. Our goal for this report was to provide, to the utmost extent of our ability, the science needed to inform sound decision-making. The best science should be policy neutral, it should give you the same answer no matter how you vote.
TR: One of the things that people coming to our site, particularly this year, are feeling, is “What can I do? How can I fix things? How can I make a change?” And feeling a little bit lost about that.
KH: Oh, yes.
TR: I was reading through some of your older interviews, and you were talking about hope and what gives you hope. One of the things you said was, “You have to offer people a vision of the world, of what the world could look like, if we could wean ourselves off of fossil fuels, if we could have a clean energy economy. We would all want to live in that world.” And I wondered if you could talk about that a little bit?
KH: Yes, I love that you brought that up. Fear and panic is great for a knee-jerk reaction but to fix this problem, we need endurance. To endure, we need hope. I really believe though that if we did have that picture, if we did understand what that world would like, who wouldn’t want it? I mean, who doesn’t want to live in a home where you grow your own energy on your own roof with your own solar shingles? And you plug in your car at home at the end of the day and you never have to visit a gas station and then wipe your hands off afterward. [laughs] That’s one of our Global Weirding videos. It’s a YouTube series that’s [part of] PBS’ digital shorts series.
One of the videos is “I’m just one person, what can I do?” and then another video is “It’s too late to fix this thing, isn’t it?” All the videos are around questions that we’ve heard people ask, and that’s why I think it’s so important to address what can we do.
TR: Just to push back a little bit, I know a lot of people say, “Oh, what can people really do? The real problem is that governments have to take action and if I go and get lightbulbs or do solar panels, is it really going to change things?”
KH: Well, that’s why, with the video, I actually conclude with what I think is the most important thing that people can do, which is talking about it. Because studies have shown that people don’t talk about this at all and they don’t think it matters to them. And so, talking about the fact that it matters, why it matters, what’s at stake, talking to people to we know, talking to elected officials — that is one of the most important things that we can do.
TR: Another thing you’ve talked about are the different things that excited you that are going on in terms of green energy — you’ve mentioned Tesla and the battery packs. And I wonder if you can talk a little bit about what new energy solutions are exciting to you right now.
KH: Oh, I’m super excited about the solar shingles. They are apparently halfway in price between a normal asphalt roof and a slate roof, and that’s without counting the energy savings. Of course, the new Tesla was just released for $35,000 or $37,000 and has a pretty amazing range. As do the Chevy and the Nissan plug-ins as well. I just feel like every time I look — and I specifically look for the hopeful news — the hopeful news is not going to be in the headlines. The headlines that you read is despairing news, it’s sad news, it’s depressing news; you have to go looking for the good news. But when you go looking for the good news, like, the Navajo Nation, this is the headline today: “The Navajo Nation is transitioning from coal to solar.” Or Elon Musk put an entire island in the South Pacific on solar and batteries, cooled it with batteries and everything. China built a giant floating solar farm on top of a coal mine that they flooded. Or the fact that people figured out ways to pull carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and turn it into blocks that can be used for construction purposes — because the problem always was, if you pull the stuff out of the atmosphere, what do you turn it into that you can actually use? Now, it’s not cost-effective yet, but you know, the first step is figuring out how to do it and then the second step is making it cost-effective. I love the fact that they’re running airplanes off algae fuel, and Oslo airport is, I think one of the only major airports in the world where they make planes refuel with algae bio-jet fuel. That’s neat.
Every month there’s a new US city committing to going 100-percent carbon free and of course, you even have Georgetown making an exit. And then you see news headlines like China’s wind company is retraining oil and coal miners to work in the wind industry. Or the solar company in San Antonio that retrained oil workers who lost their jobs when the price of oil plummeted, to do solar installations. Or, Fort Hood, the biggest military base in the country, going with wind and solar for their next electricity contract because they can save $168 million. Or the fact that pay-as-you-go solar is estimated to revolutionize energy poverty in Africa, bringing electricity to people who have never had it before.
— Katharine Hayhoe
I mean, see once I get going, [laughs] I can just keep going. All of these really cool, incredibly hopeful stories. And we have to be hearing these stories too. On my Facebook page, I monitor what things I post that are most liked and shared, the good news, hopeful stories get by far the greatest likes and shares.
People — we need that hope, we need that encouragement, we need that sense that we’re in this together and people are moving forward on this, that means that I can move forward too. What holds us back is that sense of, “Anything I do won’t make a difference,” but there’s a second part to that sentence that we don’t often verbalize: “Nothing I do will make a difference, and nobody else is doing anything either.” But when we realize, “Oh, my goodness, all these other people are doing this amazing stuff,” all of a sudden we feel hope that “maybe I can make a difference too.”
Hayhoe spoke with us on Aug. 10.




